DBH Calculator – Tree Diameter at Breast Height
Free DBH calculator & Multi-Stem DBH calculator following ISA Arborist standards. Measure tree diameter using circumference, direct measurement, or optical estimation.
- Wrap any string, rope, or shoelace around the tree trunk at 4.5 feet (breast height)
- Mark where the string meets or pinch the overlap point
- Lay the string flat and measure the length with a regular ruler
- Enter that measurement as the circumference below
Calculation Results
Multi-Stem Results
DRC Results
Optical Estimation Results
Tree Diameter Measurement: A Certified Arborist's Guide to DBH Calculation
By a Certified Arborist
With over two decades of experience in tree care and assessment, I've found that accurately measuring tree diameter is one of the most essential skills for proper tree management and health evaluation. Whether you're a homeowner concerned about a potentially hazardous tree, a landscaper planning a new project, or simply a tree enthusiast, understanding how to calculate Diameter at Breast Height (DBH) is fundamental knowledge that serves multiple purposes in arboriculture.
Why Accurate Tree Diameter Measurement Matters
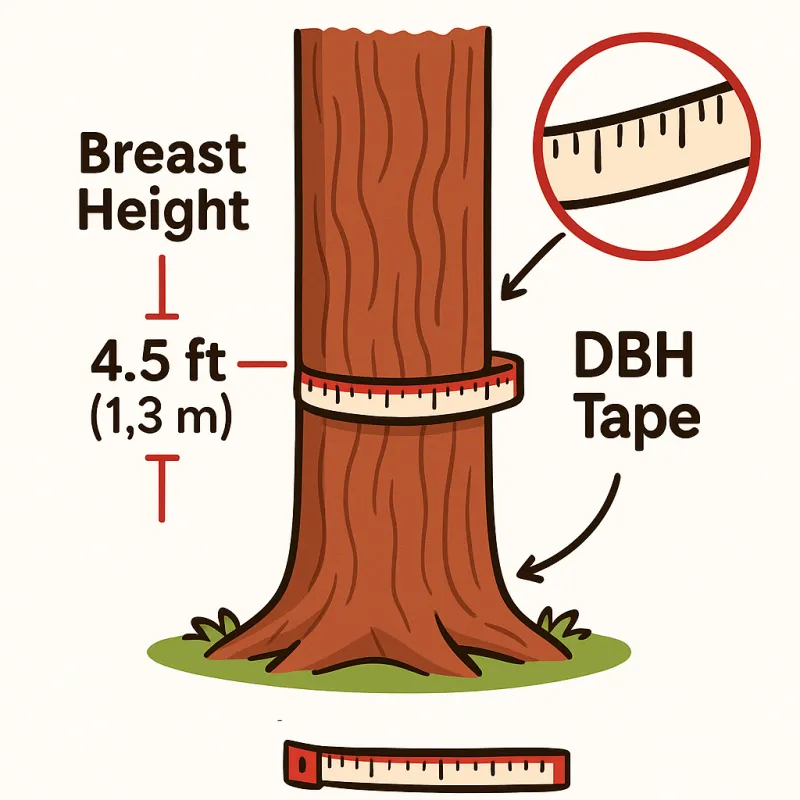
Tree diameter, particularly when measured at breast height (standardized at 4.5 feet or 1.3 meters above ground), provides critical information that informs numerous decisions in tree care:
- Tree Health Assessment - Diameter measurements taken over time help monitor growth rates, a key indicator of overall tree vitality
- Removal Cost Estimation - Most professional arborists base removal pricing partly on tree diameter, as it directly correlates with work complexity
- Structural Stability Evaluation - DBH helps determine a tree's structural capacity and potential risk factors
- Carbon Sequestration Calculation - Environmental scientists use DBH to estimate how much carbon a tree captures from the atmosphere
- Compliance with Local Regulations - Many municipalities regulate tree removal based on diameter thresholds
Arborist Insight:
In my professional experience, a surprising number of tree removals could have been avoided had the owners understood their trees' actual size and value. Accurate DBH measurement provides objective data that can guide better decision-making about tree preservation versus removal.
How to Properly Measure Tree Diameter at Breast Height (DBH)
Method 1: Using a DBH Tape (Recommended for Professionals)
Tree diameter, particularly when measured at breast height (standardized at 4.5 feet or 1.3 meters above ground), provides critical information that informs numerous decisions in tree care:
- Tree Health Assessment - Diameter measurements taken over time help monitor growth rates, a key indicator of overall tree vitality
- Removal Cost Estimation - Most professional arborists base removal pricing partly on tree diameter, as it directly correlates with work complexity
- Structural Stability Evaluation - DBH helps determine a tree's structural capacity and potential risk factors
- Carbon Sequestration Calculation - Environmental scientists use DBH to estimate how much carbon a tree captures from the atmosphere
- Compliance with Local Regulations - Many municipalities regulate tree removal based on diameter thresholds

- Position yourself on the uphill side of the tree if on a slope
- Measure exactly 4.5 feet (1.3 meters) from the ground
- Wrap the DBH tape around the trunk at this height, ensuring it remains level
- Read the diameter measurement directly from the calibrated side of the tape
Method 2: Circumference to Diameter Conversion (For Homeowners)
- Using a standard measuring tape, measure the circumference at 4.5 feet above ground
- Divide the circumference by 3.14159 (π) to calculate the diameter
- Record your measurement in inches or centimeters
For example: If your tree's circumference is 94 inches, the diameter would be 94 ÷ 3.14159 = 29.9 inches
Tree Diameter Calculator
For precise measurements, you can use this simple formula:
Diameter = Circumference ÷ π
Where π (pi) ≈ 3.14159
Special Considerations for Accurate DBH Measurement
Multi-Stemmed Trees
For trees that fork below breast height, measure each stem separately at 4.5 feet and use one of these professional methods:
Quadratic Mean Diameter: Calculate the diameter of each stem, square each value, find the average, then take the square root
Basal Area Summation: Calculate the basal area of each stem (π × r²), sum these values, then calculate the diameter of a theoretical circle with this area
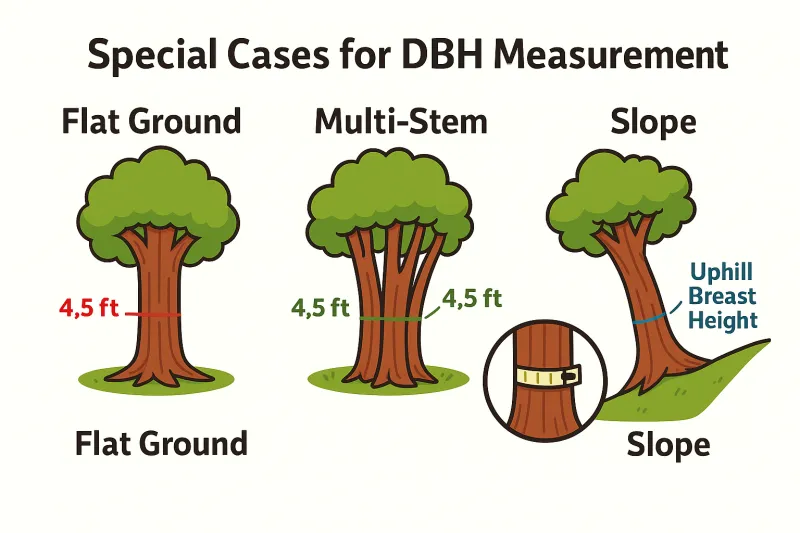
Trees on Slopes
Always measure from the uphill side of the tree, maintaining the 4.5-foot height from ground level on that side.
Trees with Abnormalities at Breast Height
If there's a bulge, branch, or deformity at 4.5 feet, measure just above or below the irregularity where the trunk resumes its typical form.
How DBH Informs Tree Care Decisions
As a practicing arborist, I regularly use DBH measurements to guide critical tree care recommendations:
| DBH Range (inches) | Common Implications | Professional Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| 1-6 | Young, establishing trees | Focus on proper structural pruning, adequate watering, mulching |
| 7-15 | Maturing trees with increasing value | Professional pruning every 3-5 years, soil management |
| 16-24 | Established trees with significant value | Root zone protection, mature tree care practices |
| 25+ | Mature, high-value specimens | Regular professional assessments, specialized care, preservation focus |
Arborist Insight:
Trees with larger diameters generally require more complex care strategies. A 30-inch diameter oak represents decades of growth that cannot be quickly replaced in the landscape. Accurate DBH measurement helps quantify this value and informs appropriate preservation efforts.
Applications of Tree Diameter Measurements
Tree Removal Cost Estimation
Most professional tree care companies use DBH as a primary factor in cost estimation. Larger diameter trees require more time, equipment, and expertise to remove safely. While many factors affect removal costs (location, accessibility, species), diameter provides a reliable starting point for estimates.
Tree Ordinance Compliance
Many municipalities have tree protection ordinances that regulate removal based on diameter thresholds. In my experience, having accurate DBH measurements can help homeowners navigate permit requirements and potentially avoid fines for unauthorized removals.
Tree Valuations
When conducting appraisals for insurance claims, property disputes, or development planning, DBH is a fundamental input in tree valuation formulas. Precise measurements ensure fair and defensible valuations that accurately reflect a tree's contribution to property value.
Frequently Asked Questions About Tree Diameter Measurement
The 4.5-foot standard (called "breast height") was established to create consistency in forestry measurements. Measuring at this height avoids the irregular flaring that often occurs at the tree base, providing a more uniform point of reference for comparative measurements across different trees and species.
While there is a relationship between diameter and age, it's not precise enough for accurate aging. Growth rates vary significantly based on species, site conditions, and climate. Some species like silver maple grow quickly (adding 1+ inch diameter annually), while others like oak may add only 1/4 inch per year. As a rule of thumb, age estimation from diameter should be considered approximate at best.
Diameter is one factor in comprehensive tree risk assessment. Larger diameter trees generally pose greater potential consequences if they fail, but diameter alone doesn't determine risk. Professional arborists evaluate multiple factors including structural defects, crown architecture, and site conditions alongside diameter measurements to assess risk holistically.
For most homeowners, annual measurements are sufficient to track growth trends. Mark the exact point of measurement (4.5 feet) with a small, non-damaging indicator to ensure you're measuring at the same point each time. Consistent annual measurements can help detect growth rate changes that might indicate developing health issues.
Need Professional Tree Assessment?
While DIY measurements provide valuable information, nothing replaces a comprehensive evaluation by a certified arborist. Professional assessment goes beyond diameter to evaluate overall health, structural integrity, and specific care recommendations.
Conclusion: The Importance of Accurate Tree Measurements
Throughout my career as an arborist, I've seen countless examples of how precise tree diameter measurements inform better decision-making about tree care, preservation, and removal. Whether you're managing a small residential property or overseeing a large urban forest, understanding and accurately measuring DBH provides an objective foundation for tree management.
By following the measurement techniques outlined above, you'll be equipped with valuable data that can help preserve tree health, comply with local regulations, and make informed decisions about the remarkable trees that enhance our environment and communities. Remember that while diameter measurements are important, they're just one component of comprehensive tree care—when in doubt, consult with a certified arborist who can provide guidance specific to your trees and circumstances.
